| Name | Image | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spotting Squats |  |
|
Details |
| 2 person spotting |  |
With 2 people you have the security that if the bar drops completely from the squatter, the spotters will be able to safely take the load of the weight. Positioning: stand at opposite ends of the bar, with feet shoulder width apart and knees slightly flexed. Hold hands in a cupped position ~ 2-3″ below the ends of the bar. As client starts moving down, continue to bend through the knees, ensuring your hands remain 2-3″ below the bar. If client struggles/fails, both spotters should grasp the bar and assist the client to lift bar back into the starting position, ensuring they employ a similar/steady lifting cadence. Critical point: It is absolutely necessary that spotters communicate. Both spotters should have a signal to know when to jump in safely. If one spotter decides to help while the other doesn’t, the lifters balance will be thrown off and they risk significant injury. |
Details |
| Barbell Bench Press |  |
1. Stand behind your lifter here. You might want to ask the lifter if they need a “lift-off” (an assist lifting the bar off the rack before the first rep begins). 2. You should also ask the lifter how soon they would like your help: immediately or whether you should let them struggle with the weight before jumping in. Generally, for a novice you should jump in immediately, whereas you might permit an advanced lifter to struggle with the weight for a bit. 3. From there, let the athlete lift and when you see him or her reach a point where they are unable to move the bar, use a reverse grip (one overhand and one underhand), to ensure you can pull the bar up should the lifter fail during the lift. |
Details |
| Dumbbell Shoulder Press |  |
The trainer (standing behind the bench) should assist the client to get the weights into position. All spotting assistance should be provided by grabbing client’s wrist/forearm (and not spotting at the elbow). |
Details |
| Dumbbell Chest Press |  |
The trainer (standing behind the bench near the client’s head) should assist the client to get the weights into position. All spotting assistance should be provided by grabbing client’s wrist/forearm (and not spotting at the elbow). |
Details |
| Mirror Client Level |  |
Details | |
| Travel alongside client |  |
Details | |
| Treadmill |  |
Details | |
| Cables | Details | ||
| Suspension Training | Details | ||
| Instability training | Details | ||
| Band/Tubing Anchoring | Details | ||
| Consider self-spotting option | 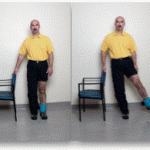 |
Provide a chair or dowel or move near a wall or counter top to allow client to self-spot / secure their position and set-up. |
Details |
